Ever since the advent of cloud technologies, their adoption and usage have grown exponentially. Leveraging it has helped with innovation, scalability and efficiency in business operations across industries.
However, as the cloud adoption has grown, so has it’s cost overall! Gartner predicts that global spending on public cloud services will reach $723 billion in 2025, reflecting the scale of investment businesses are making. Industries such as Retail, Consumer Packaged Goods (CPG), and Telecommunications are particularly heavy cloud users, with cloud expenses accounting for up to 30% of their IT budgets, according to McKinsey. Moreover, the annual cloud spending of enterprises in these sectors is growing at rates of 20-30%, highlighting the urgency of addressing cloud cost optimization.
What factors have led to it becoming a major component of IT budgets?
Cloud services have become a major driver of IT budgets due to several key factors. Rising costs often result from underutilized or idle resources, such as over-provisioned virtual machines operating at low utilization but still accruing expenses. The absence of a structured, scalable model frequently leads to reactive purchasing of additional servers, resulting in inefficient resource allocation.
Redundancies within systems also play a significant role, with overlapping solutions deployed by different teams inflating costs unnecessarily. Mismanagement of pricing models further contributes to budget strain, as organizations frequently fail to take advantage of cost-saving options like reserved or spot instances. Additionally, data transfer costs can add up unexpectedly, driven by the high volume of inter-system communication and data movement.
Another critical factor is insufficient visibility into resource usage and spending patterns. Without robust monitoring and reporting, organizations struggle to identify inefficiencies and uncover potential savings opportunities, allowing costs to escalate unchecked.

The complexity involved
Optimizing cloud spending presents challenges due to complex billing structures and pricing models. Cloud providers offer on-demand pricing (averaging $0.10 to $0.20 per hour), reserved instances (savings up to 72% over on-demand rates), and spot instances (up to 90% cheaper), each requiring careful evaluation.
Resource sprawl arises as multiple teams independently provision resources, leading to inefficiencies. Research from Flexera’s State of the Cloud Report 2024 reveals that organizations waste approximately 27% of their cloud budgets on idle or underutilized resources. Also, 71% Enterprises are prioritizing optimizing the existing use of cloud (cost savings) as the top initiative for the next year.
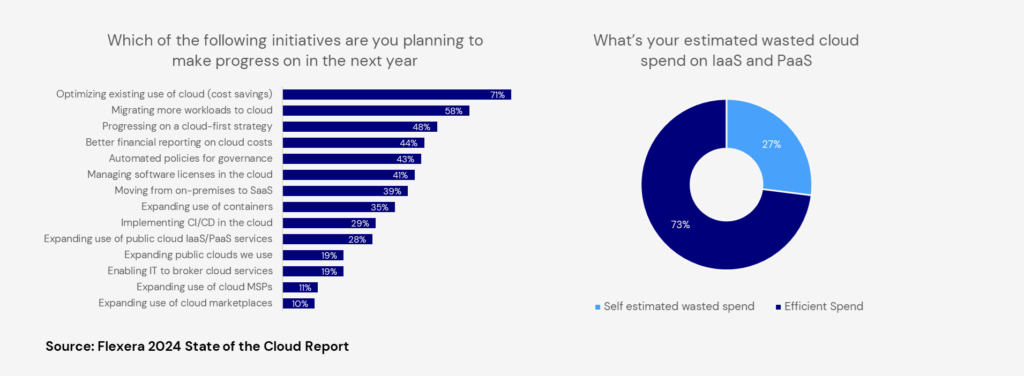
Compounding the problem is shadow IT, where unmonitored services create hidden costs further driving up expenses. Additionally, lack of billing transparency complicates cost management, with organizations facing an average of 4,000 line items per bill. Unchecked resource allocation during peak periods can also escalate costs by 30-50% when not scaled back.
Key levers for optimizing cloud spends
• Pricing and provider evaluation:
- Compare pricing across providers for specific services. For example, storing 1 TB of data on AWS S3 Standard costs around $23 per month, while Google Cloud Storage Standard is approximately $20 per month (note this figure is for storage cost only while there might be other factors such as service breadth and depth, availability zones, etc. which might drive the overall choice). Assess reserved, on-demand, and spot pricing models to choose cost-effective solutions tailored to your workload needs.
• Resource optimization and scalability:
- Conduct regular performance assessments to right-size resources and eliminate idle or oversized instances. Implement auto-scaling policies to dynamically adjust resources based on demand, preventing over-provisioning during off-peak hours while maintaining performance during peak periods.
• Governance and data security:
- Establish governance frameworks with role-based access controls, resource tagging, and strict budget thresholds. Ensure compliance with data regulations like GDPR or HIPAA to avoid risks while optimizing costs. Encryption and secure storage of sensitive workloads are essential during migrations or cost-cutting measures.
• Monitoring and automation tools:
- Use tools like AWS Cost Explorer or Azure Cost Management to track and analyze spending. Automation tools can schedule resource shutdowns for non-production environments and enforce efficient scaling, leading to significant savings.
• Adopt a multi-cloud strategy:
- Distribute workloads across multiple providers to take advantage of cost and performance benefits. For instance, using one provider for storage and another for compute can optimize costs while enhancing performance.
Conclusion
Cloud spend optimization is no longer optional; it is a critical business imperative in an era of rising cloud adoption and dynamic business demands. Effective cost management not only curtails unnecessary spending but also ensures that organizations can allocate resources toward innovation, scalability, and resilience. By adopting a proactive, long-term approach, businesses can unlock the full potential of their cloud investments while maintaining financial discipline.
Successful optimization requires a comprehensive strategy that includes analyzing usage patterns, setting clear governance policies, and leveraging advanced tools for monitoring and automation. Organizations must also remain agile to adapt to changing workloads, embrace multi-cloud strategies for cost and performance benefits, and prioritize data security to mitigate risks associated with cost-saving measures.
Begin your journey today by assessing your current cloud footprint and implementing the strategies that align with your business goals and vision.

